Process Of Dna Replication Ligase | Instead, another enzyme, dna ligase, seals off the nicks by. This ensures that the insert will be added in the correct orientation and prevents the vector from ligating to itself during the ligation process. Dna cloning and recombinant dna. Dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical copies of dna from its original or mother dna is known as dna replication. The process of dna replication can be summarized as follows once replication is completed, the rna primers are replaced by dna nucleotides and the dna is sealed with dna ligase.
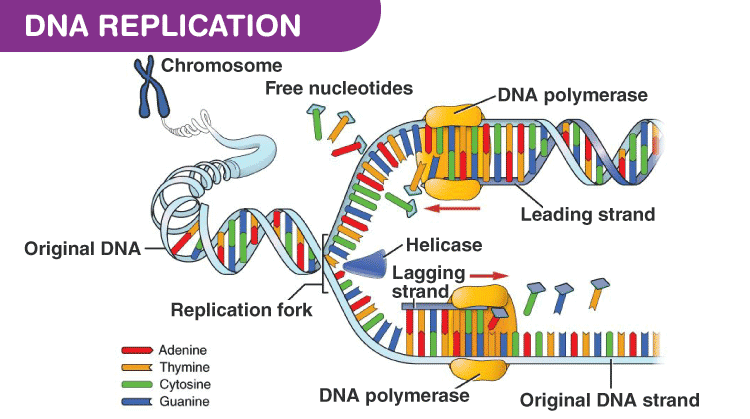
Dna replication is the process in which a dna molecule makes a copy of itself. Dna polymerase adds nucleotides to the deoxyribose (3') ended strand in a 5' to 3' direction. The process that copies dna is called replication. This is the currently selected item. Dna replication is termed semiconservative replication because each newly formed molecule of dna has one strand conserved from the along a strand of dna, replication begins at numerous origins of replication.
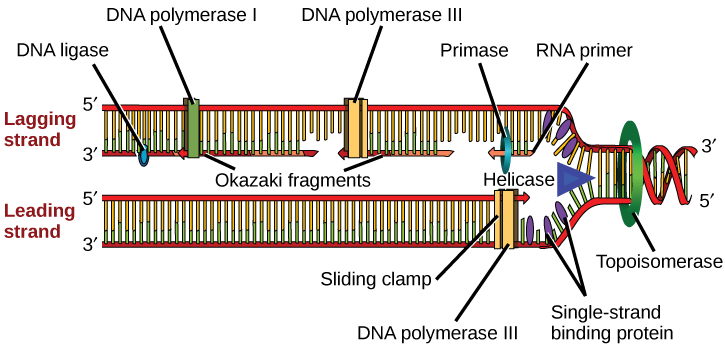
Dna polymerases can't seal up the nicks that result from the replacement of rna primers with dna. In general, eukaryotic dna ligases are much larger than their prokaryotic counterparts; Dnap i remove the rna primers and replace the existing gap with the appropriate deoxynucleotides. Then, dna polymerase i replaces the rna primers with dna nucleotides, and an enzyme called dna ligase has to connect all the fragments to create a. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. Dna replication is the process in which new copy of dna is produced from parent dna. The cellular processes of dna replication, recombination, and repair generate breaks in the phosphate. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. The process of dna replication includes control mechanisms to keep the genetic information as stable as possible, but errors (e.g., the incorporation of a wrong base) still occur. External factors as well as internal cellular processes lead to alterations in the chemical structure of dna. Dna replication is the process by which an organism duplicates its dna into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells. This is the currently selected item. Replication is a process in which a dna molecule is copied.
This results in two exact copies of the original dna with. Two enzymes, a polymerase and a dna ligase, replace the rna. There are several enzymes involved in the process of dna replication. Dna ligase enzymes seal the breaks in the backbone of dna that are caused during dna replication, dna damage, or during the dna repair process. Dna replication is the process by which dna makes a copy of itself during cell division.
Dna replication begins with the unzipping of the parent molecule as the hydrogen bonds when the process is complete, two dna molecules have been formed identical to each other and to the parent molecule. Due to initiation of replication at multiple locations, the process is completed within one hour. In general, eukaryotic dna ligases are much larger than their prokaryotic counterparts; This is the currently selected item. Ligase fuses the last remaining segment by creating the final phosphodiester linkage. Dna polymerases can't seal up the nicks that result from the replacement of rna primers with dna. 2.7 dna replication, transcription, translation. Dna replication is a vital process in the reproduction of cells. On average, around one mistake is made for every 10 billion nucleotides that are replicated. The smallest dna ligase is produced by the bacteriophage t7. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. Translation is the process of protein synthesis in which the genetic information encoded in mrna is translated into. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together.
Genetic information in dna can be accurately dna ligase (another enzyme) joins all the okazaki fragments together. This is the currently selected item. During the process of replication, these sticky single stranded dna are prevented to become duplex by special proteins called as single strand binding proteins gap created by primer is filled by adding nucleotides at 3′ end. There are several enzymes involved in the process of dna replication. The process of dna replication can be summarized as follows once replication is completed, the rna primers are replaced by dna nucleotides and the dna is sealed with dna ligase.

Dna polymerase binds to the leading strand and then 'walks' along it, adding new complementary finally, an enzyme called dna ligase seals up the sequence of dna into two continuous double strands. The two copies of dna produced contain one original strand and one new strand. The cellular processes of dna replication, recombination, and repair generate breaks in the phosphate. Dnap i remove the rna primers and replace the existing gap with the appropriate deoxynucleotides. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. Dna ligase enzymes seal the breaks in the backbone of dna that are caused during dna replication, dna damage, or during the dna repair process. Due to initiation of replication at multiple locations, the process is completed within one hour. Dna replication is the process in which new copy of dna is produced from parent dna. The human dna is copied at about 50 base pairs per second. Dna polymerase adds nucleotides to the deoxyribose (3') ended strand in a 5' to 3' direction. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell.
The process that copies dna is called replication ligase dna replication. One of the key players is the.
Process Of Dna Replication Ligase: Restriction enzymes & dna ligase.
comment 0 Comments
more_vert